√画像をダウンロード p-xylene c13 nmr 138956-P-xylene h nmr
1H NMR 2 (Varian Associates NMR Spectra Catalogue) C13 NMR 297 (Johnson and Jankowski, Carbon13 NMR Spectra, John Wiley and Sons, New York) Raman 81 (Dollish et al, characteristic Raman Frequencies of organic compounds, John Wiley and Sons, New York)NMR spectra were obtained using a Bruker AVANCE 400 MHz spectrometer Data were collected at ambient temperature and varied by ±2 °C 1H NMR spectra were obtained at pxylene C (1,4) 5158 methyl acetate OCH 3 2142 isopropyl acetate CH)) 1 BNMRChemicalShiftsofCommon LaboratorySolventsasTraceImpurities HugoEGottlieb,*VadimKotlyar,and AbrahamNudelman* DepartmentofChemistry,BarIlanUniversity,
Bmse0004 P Xylene At Bmrb
P-xylene h nmr
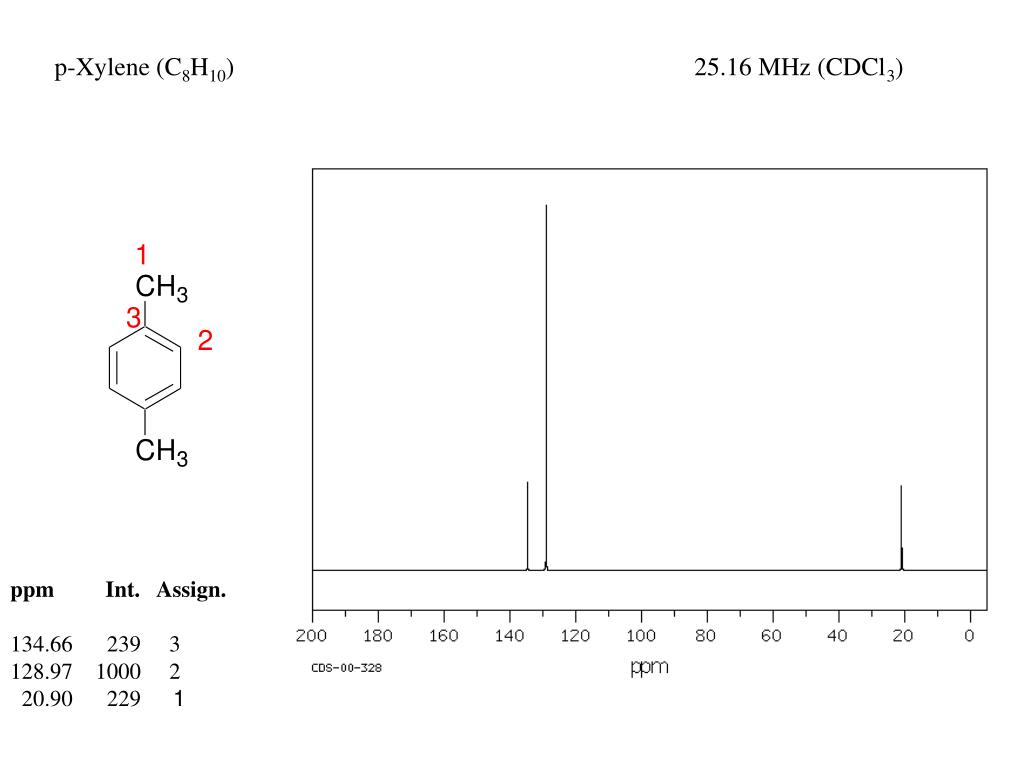
P-xylene h nmr-The clathrate formation of 3 with toluene and pxylene has been studied with C13 CPMAS NMR spectroscopyINTENSITIES OF THE SIGNALS (PEAK AREA AND PROTON COUNTING)Consider NMR spectra of toluene and pxylene (pxylene) Each compound possess two type of proton (1)Methyl (2)aromatic protons These protons shows two signal in NMR spectra nearly δ 23 and δ 72 values Intensities of methyl proton and aromatic proton signal in NMR spectra on


Http Www Users Miamioh Edu Gungbw Chm255 Html Pdfs Nmr Pdf
NMRChemicalShiftsofCommon LaboratorySolventsasTraceImpurities HugoEGottlieb,*VadimKotlyar,and AbrahamNudelman* DepartmentofChemistry,BarIlanUniversity,Publications Describing the STAR Format;NMRSTAR 32 Dictionary Documentation;
Ai3029x benzene,dimethylcaswellno906 Dimethylbenzene (mixed isomers) Dimethylbenzenes except pxylene, 1H NMR 2 (Varian Associates NMR Spectra Catalogue) C13 NMR 297 (Johnson and Jankowski, Carbon13 NMR Spectra, John Wiley and Sons, New York)The basic chemistry of pxylene, 3,6dibromopxylene, 3,6dichloropxylene and 3,6difloropxylene in terms of reactivity, stability and interaction have been discussed in this study extensively Optimization of this compounds was done with GAUSSIAN 09 of density functional theory (DFT) method of LYP/6311G(d,p) basis setNuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 1 Background Over the past fifty years nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, commonly referred to as nmr, has become the preeminent technique for determining the structure of organic compounds Of all the spectroscopic methods, it is the only one for which a complete analysis and interpretation of
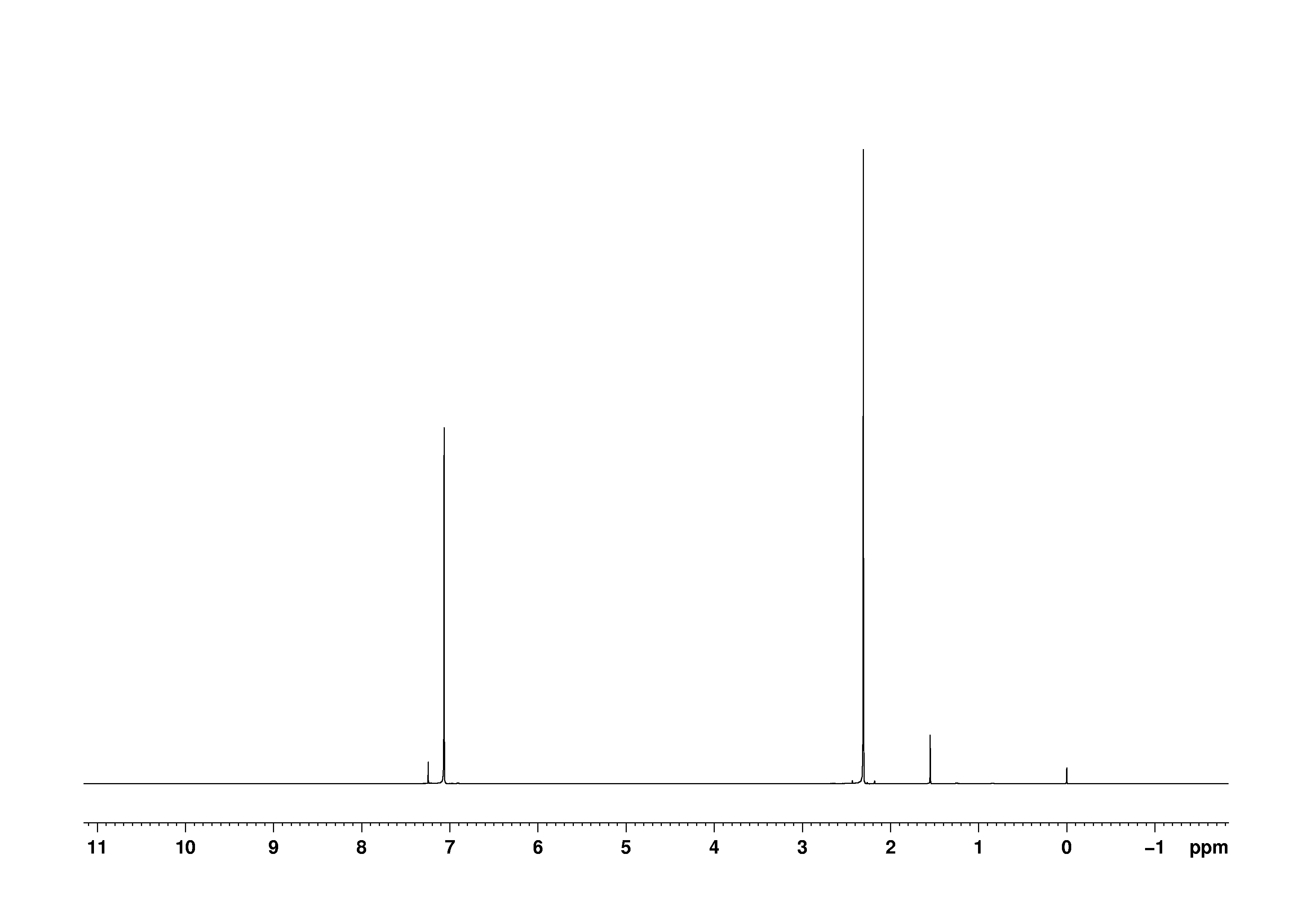
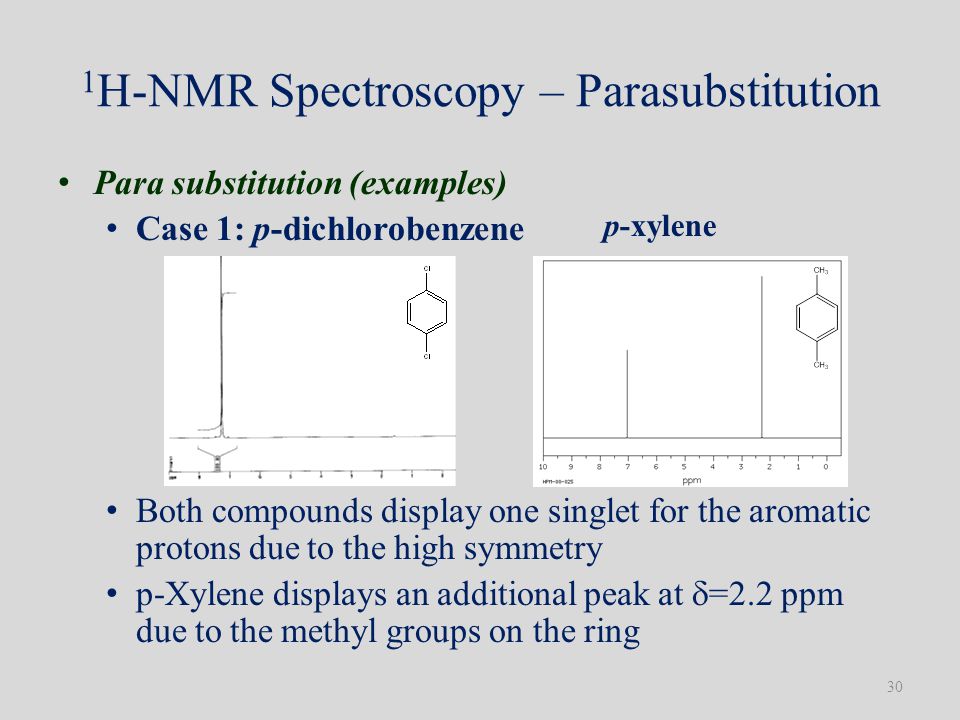
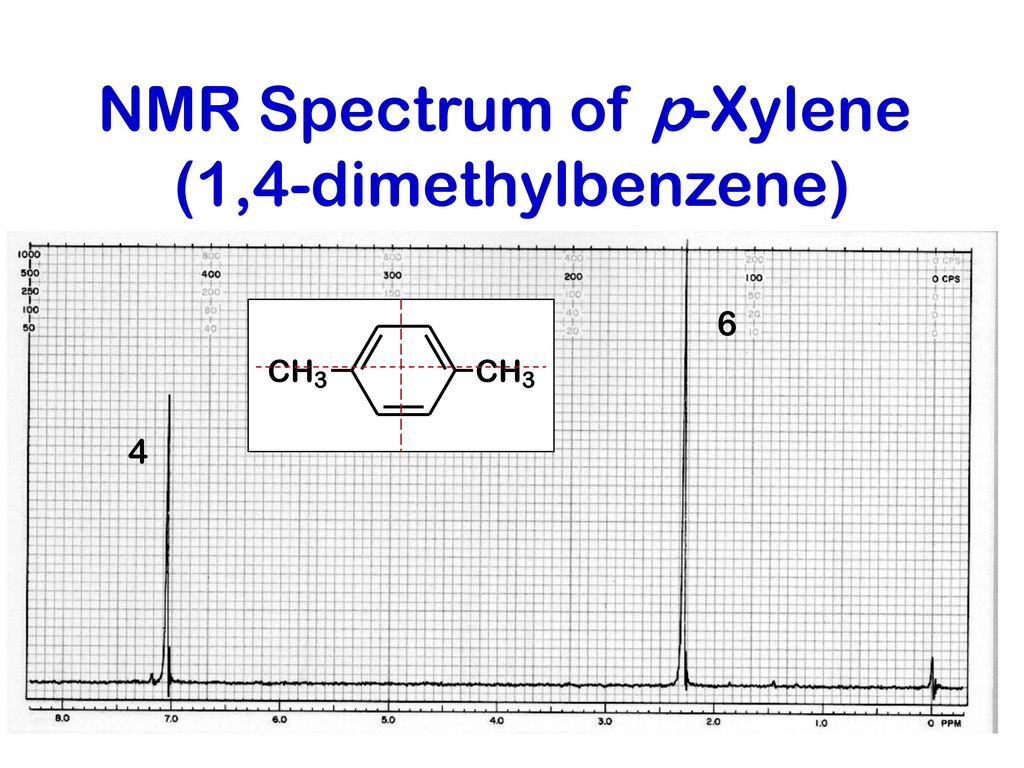
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy NMR Chemical Shift Values Table In the previous post, we talked about the principles behind the chemical shift addressing questions like how the ppm values are calculated, why they are independent of the magnetic field strength, and what is the benefit of using a more powerful instrumentEach isomer of xylene produces a slightly different 1H NMR spectrum The highly symmetric pxylene produces two signals, one aliphatic signal due to the substituent methyl protons, and a second aromatic proton signal The lower symmetry oxylene and pxyleneIn nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic field Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule Chemical shifts are also used to describe signals in other forms of spectroscopy such as photoemission spectroscopy


P Xylene 13c Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase


Solved Xylene Dimethylbenzene Has Three Isomeric Forms Chegg Com
And incorrect enough for me to have a rant about NMR teaching at the introductory level Some background knowledge before tackling your molecules 'Environments' is a vague term, often misused and misunderstood, unless you specify what type of environment chemical or magnetic As an argument about chemical environments alone, you need onlyThe pxylene adduct of Dianin's compound was studied by solid state NMR molecular modelling Molecular potential calculations were performed considering a pxylene guest molecule in a single hostChemicalBook ProvidemXylene(10) 1H NMR,IR2,MS,IR3,IR1,1H NMR,Raman,ESR,13C NMR,Spectrum


Http Www Users Miamioh Edu Gungbw Chm255 Html Pdfs Nmr Pdf


1h Nmr Ppt Video Online Download
SPXYLENE() 13 C NMR Related Products 4tertButylbenzyl bromide() 13 CNMR 4tertButylbenzyl bromide()This organic chemistry video tutorial explains how to determine the number of signals in a H NMR spectrum as well as a C NMR spectrum using symmetry and theIn particular the 13 C NMR signals in the range of 159–167 ppm (see C5 in Table 2), present in the spectra of all azomethines and ketimines, confirm the existence of the imine group carbon atoms and are upfield shifting for the compounds with the diketone subunitsFor example, in the spectrum of K1 a clear signal characteristic of the carbon atom in the C N group (see C5 in Table 2) is


P Xylene 13c Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase



Summary Of Critical Parameters For O Xylene M Xylene P Xylene And Download Table
Solvent Formula 1 HNMR shift (ppm) 13 CNMR shift (ppm) Multiplet J CD (Hz) mp (o C)bp(o C)Comments Chloroformd CDCl 3 724 770 triplet 3264 61Structure and properties Index of refraction, n D at °C Dielectric constant, ε r 22 ε 0 at °C Surface tension 2992 dyn/cm at 5 °C 27 dyn/cm at °CThe 1H NMR singlet for the SiMe 3 groups of TSP and sodium 3(trimethylsilyl)propanesulfonate were within ±002 ppm10 For 13C NMR spectra in D 2 O, 5 μL of methanol was added to each corresponding NMR sample, and its methyl resonance was set to 4950 ppm RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 1H NMR spectral data for industrially preferred solvents in six


Solved Problem 13 18 How Many Peaks Would You Expect In T Chegg Com



2 Ethyl P Xylene 1758 9 13c Nmr
In this video series I'll teach the techniques I use to interpret NMR spectra If you watch the complete series, you'll have all the skills you need to inte2,5Dichloropxylene 1 Product Result Match Criteria Product Name, Property Linear Formula (CH 3) 2 C 6 H 2 Cl 2 Molecular Weight CAS Number D ;ChemicalBook ProvidemXylene(10) 1H NMR,IR2,MS,IR3,IR1,1H NMR,Raman,ESR,13C NMR,Spectrum



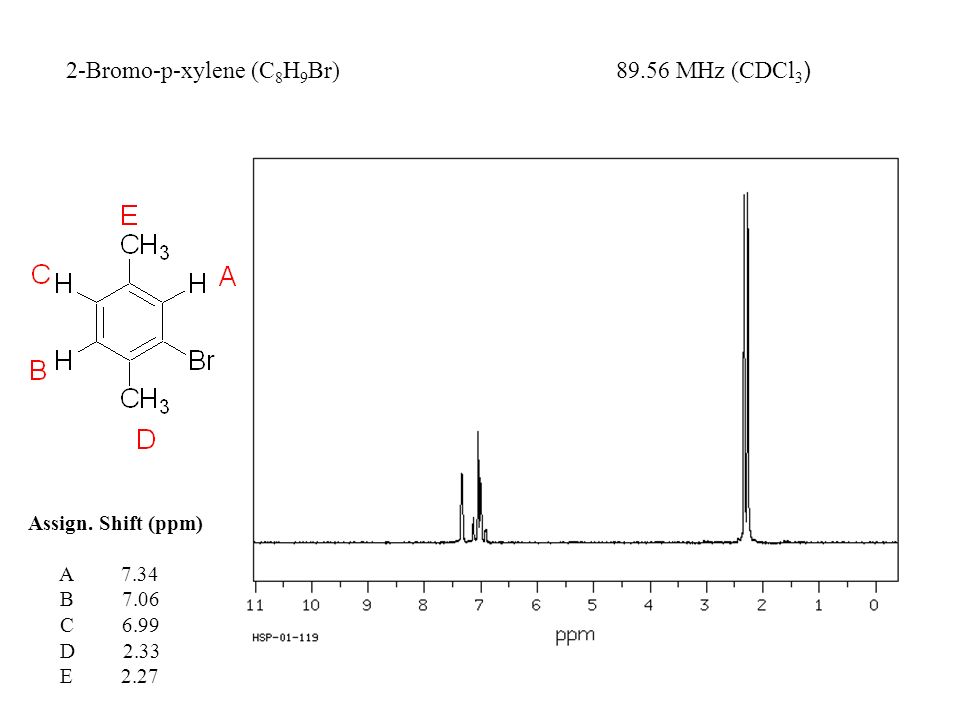
2 Bromo P Xylene Spectrabase



Bmse0004 P Xylene At Bmrb
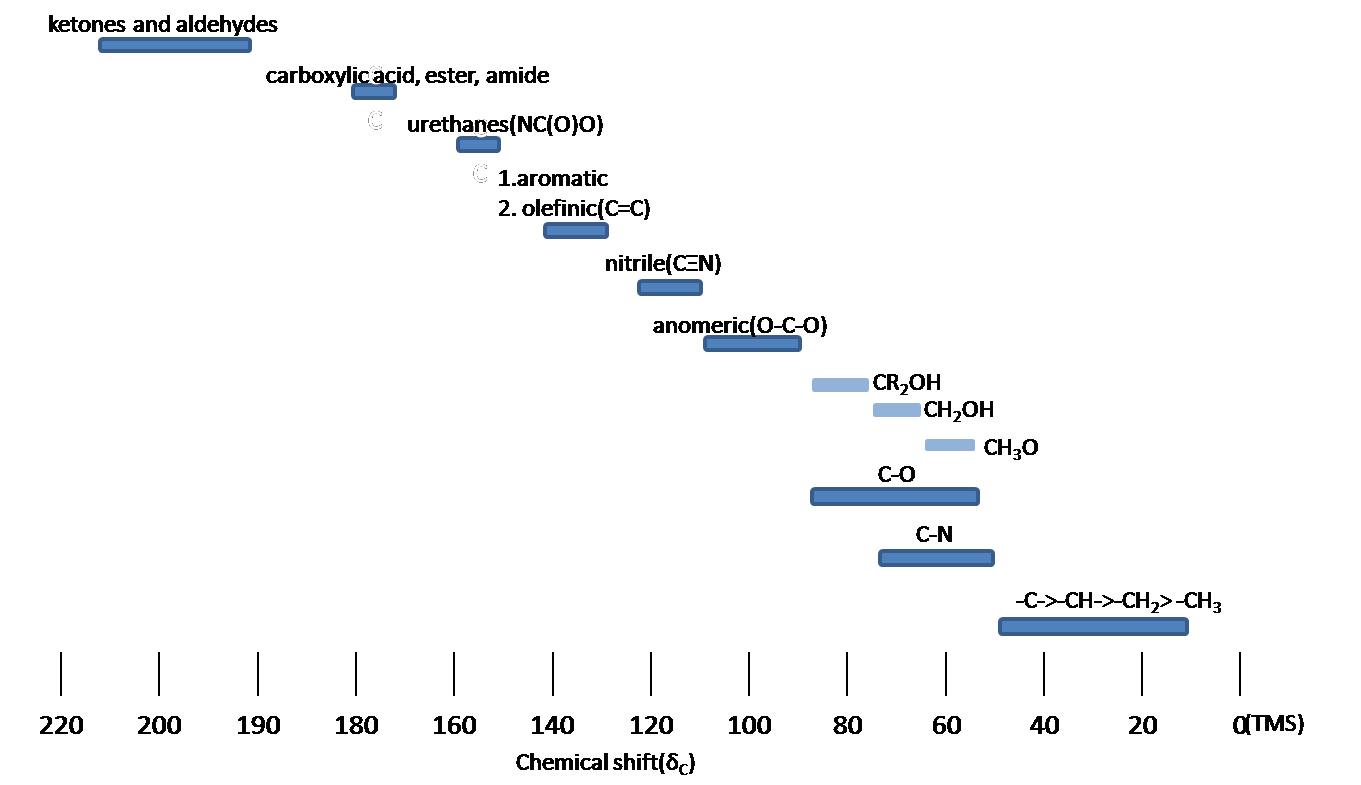
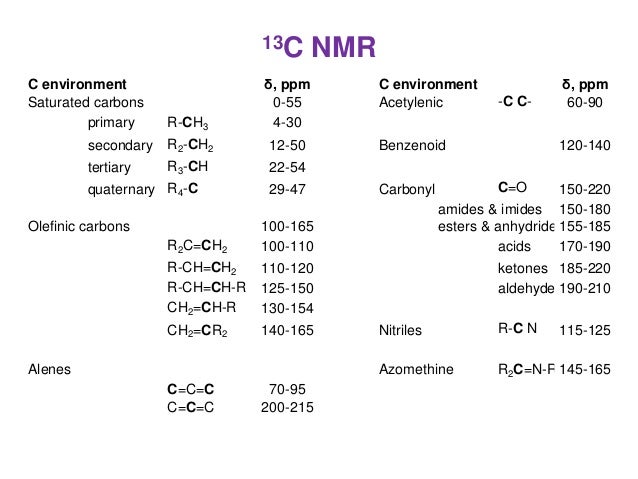
NMRSTAR 32 Complete Annotated Schema;13 C nucleus is about 400 times less sensitive than H nucleus to the NMR phenomena Due to the low abundance, we do not usually see 13 C 13 C coupling Chemical shift range is normally 0 to 2 ppm13C NMR of pXylene CH3 CH3 13C NMR of oXylene CH3 CH3 13C NMR of mXylene CH 3 CH 3 13 C NMR of oTolualdehyde CH 3 CHO 13 C NMR of Acetophenone CH 3 O 13 C NMR of nButyl Ether O 13 C NMR of 2furancarboxylic acid octyl ester O O O 13 C NMR Chemical Shifts DEPT CNMR Spectra Normal 13C spectra are broadband decoupled With the


Quiz 13



P Xylene 106 42 3 13c Nmr
NMR Data Formats NMR Data Formats;Two signals Also, why does CDCl3 show up as a triplet?Compound pToluidinewith free spectra 84 NMR, 9 FTIR, 1 Raman, 2 Near IR, and 21 MS


13 11 Characteristics Of C Nmr Spectroscopy Chemistry Libretexts



Sections Of 1 H Nmr 600 Mhz Spectra For 1111 And 2112 In Download Scientific Diagram
View at https//couchcheminfoorg/cheminfopublic/bac9d7212f8e5ae8167a45f3c/viewjson could not be loadedhttps//couchcheminfoorg/cheminfopublicNuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy NMR Chemical Shift Values Table In the previous post, we talked about the principles behind the chemical shift addressing questions like how the ppm values are calculated, why they are independent of the magnetic field strength, and what is the benefit of using a more powerful instrumentThe pxylene adduct of Dianin's compound was studied by solid state NMR molecular modelling Molecular potential calculations were performed considering a pxylene guest molecule in a single host


Structure Determination Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Ppt Download



O Xylene 95 47 6 1h Nmr
Compound pXylenewith free spectra 60 NMR, 19 FTIR, 2 Raman, 2 Near IR, and 23 MSAlthough orthoxylene (isomer B) will have a proton nmr very similar to isomer A, it should only display four 13 C nmr signals, originating from the four different groups of carbon atoms (colored brown, blue, orange and green) The methyl carbon signal will appear at high field (near ppm), and the aromatic ring carbons will all give signals having δ > 100 ppmIn C13 NMR, you cannot draw any simple conclusions from the heights of the various peaks Example \(\PageIndex{2}\) C13 NMR spectrum for 1methylethyl propanoate 1methylethyl propanoate is also known as isopropyl propanoate or isopropyl propionate


C 13 Nmr Chemistry Libretexts


Exam 2 Answer Key
Now that we have had an introduction to key aspects of 1 H NMR spectra (chemical shift, peak area, and signal splitting), we can start to apply 1 H NMR spectroscopy to elucidating the structure of unknown compounds The following steps summarize the process Count the number of signals to determine how many distinct proton environments are in the molecule (neglecting, for the time being, the1H NMR 2 (Varian Associates NMR Spectra Catalogue) C13 NMR 297 (Johnson and Jankowski, Carbon13 NMR Spectra, John Wiley and Sons, New York) Raman 81 (Dollish et al, characteristic Raman Frequencies of organic compounds, John Wiley and Sons, New York)The same solvents are used for 13 C NMR spectra, so the same rules about splitting patterns apply here also It used to be common practice to add Me 4 Si, or related compounds, as an internal reference standard for 1 H and 13 C NMR spectra with the proton signal occurring at 00 ppm and the carbon signal occurring at 00 ppm in the 13 C NMR



How To Read Carbon 13 Nmr Spectrums Predict Signal S M Xylene P Xylene O Xylene Youtube


1h Nmr Spectra Interpretation Ppt Download
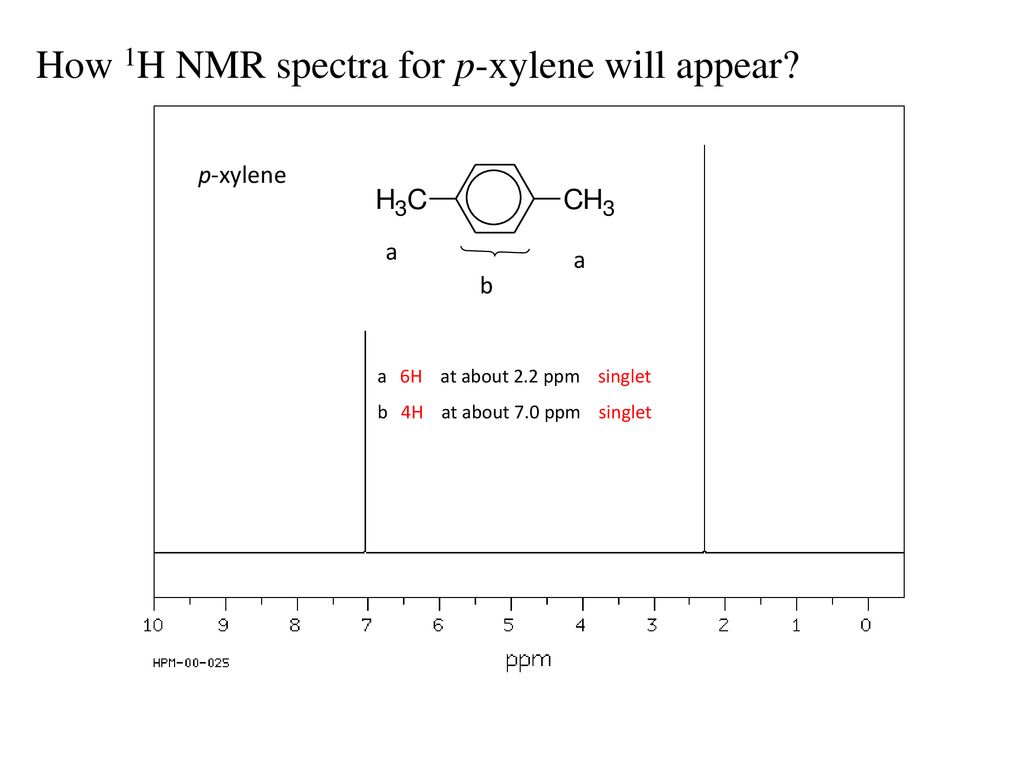
Subsequently, question is, how many NMR signals does P xylene have?ChemicalBook ProvideoXylene() 13C NMR,IR2,MS,IR3,IR1,1H NMR,Raman,ESR,13C NMR,SpectrumChemical Shifts The NMR spectra is displayed as a plot of the applied radio frequency versus the absorption The applied frequency increases from left to right, thus the left side of the plot is the low field, downfield or deshielded side and the right side of the plot is the high field, upfield or shielded side (see the figure below)


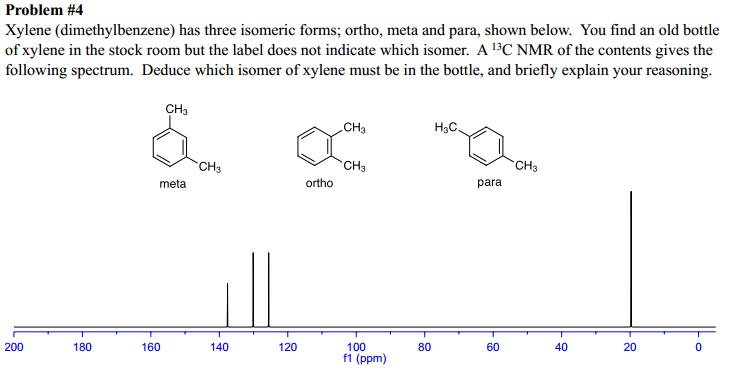
Solved The Three Isomers Of Dimethylbenzene Are Commonly Named Chegg Com



2 5 Dibromo P Xylene 13c Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase
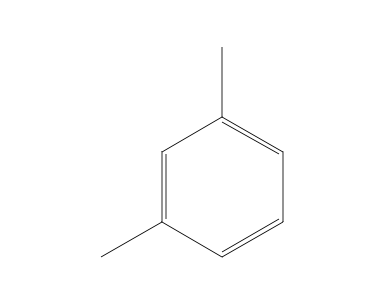
The lowtemperature structure and dynamics of guest molecules of pxylene incorporated in the isopropylcalix4 arene(21) pxylene complex have been investigated by solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) Using onedimensional H1decoupled C13 crosspolarization magicanglespinning (MAS) NMR and twodimensional H1C13 correlation spectroscopy, a full assignment of the C13 and H1It comes from splitting from deuterium The formula for splitting is 2nI 1, where n is the number of nuclei, and I is the spin typeMXylene (metaxylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbonIt is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenesThe mstands for meta, indicating that the two methyl groups in mxylene occupy positions 1 and 3 on a benzene ringIt is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, oxylene and pxylene


Pubs Acs Org Doi Pdf 10 1021 Acs Oprd 5b


Quiz 12
1H NMR 2 (Varian Associates NMR Spectra Catalogue) C13 NMR 297 (Johnson and Jankowski, Carbon13 NMR Spectra, John Wiley and Sons, New York) Raman 81 (Dollish et al, characteristic Raman Frequencies of organic compounds, John Wiley and Sons, New York)Welcome to Spectral Database for Organic Compounds, SDBS This is a free site organized by National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), JapanGHS Hazard Statements H225 (100%) Highly Flammable liquid and vapor Danger Flammable liquidsH302 (100%) Harmful if swallowed Warning Acute toxicity, oralH304 (9479%) May be fatal if swallowed and enters airways Danger Aspiration hazardH311 (4062%) Toxic in contact with skin Danger Acute toxicity, dermalH411 (5521%) Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects Hazardous to


M Xylene C6h4 Ch3 2 Pubchem



P Xylene 106 42 3 1h Nmr
4tertButyloxylene 1 Product ResultChemicalBook ProvideoXylene() 13C NMR,IR2,MS,IR3,IR1,1H NMR,Raman,ESR,13C NMR,SpectrumDeuterated solvents, where 99% of the protons are replaced with deuterium, are used as a solvent in NMR spectroscopy SigmaAldrich is committed to providing the widest range of NMR solvents for routine use with excellent chemical purity and with the highest isotopic enrichment



5 6 La Espectroscopia 13c Nmr Libretexts Espanol


Q Tbn And9gcsd4 Tsyx6hojmkwm2j9zekqdkncakj4rwbipluop53oivy22as Usqp Cau



Integration Of Proton Nmr Absorptions Mcc Organic Chemistry



1 4 Dibromo 2 5 Dimethylbenzene 1074 24 4 13c Nmr


Canvas Wisc Edu Courses Files Download Wrap 1


Ppt 1 H Nmr Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



X Ray Profiles Of Sps P Xylene And Sps M Xylene Systems At Room Download Scientific Diagram



13 11 Characteristics Of C Nmr Spectroscopy Chemistry Libretexts



C13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance


Canvas Wisc Edu Courses Files Download Wrap 1



Identifications And Fundamental Constants Of O Xylene M Xylene Download Table



P Xylene 13c Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase



Solved The Three Isomers Of Dimethylbenzene Are Commonly Chegg Com


The Chemical Structure Of O Xylene M Xylene P Xylene And Ethylbenzene Download Scientific Diagram


Pubs Acs Org Doi Pdf 10 1021 Acs Oprd 5b



11 Points The 1h Nmr 13c Nmr Mass Spectra And Ir Spectra For A Mystery Homeworklib



Check Your Unknown 3 Mass Spectrum Ppt Video Online Download


Introduction To Nmr Spectroscopy Ppt Download



Hexamethylbenzene 87 85 4 13c Nmr


Solved The Three Isomers Of Dimethylbenzene Are Commonly Named Chegg Com



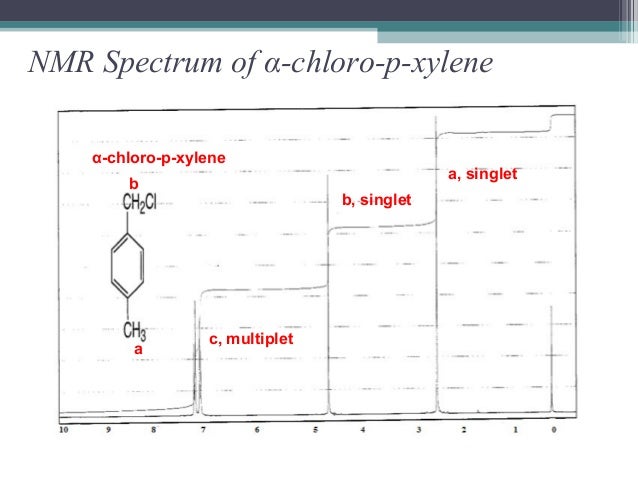
Alpha Alpha Dichloro P Xylene 623 25 6 1h Nmr



The High Resolution Solid State 13 C Nmr Spectra Of Sps M Xylene And Download Scientific Diagram


1h Nmr Ppt Video Online Download


Ozpgcz7b1hsixm
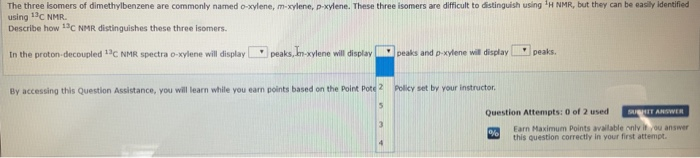


Solved Nmr But They Can Be Easily Identite The Three Iso Chegg Com



M Xylene 108 38 3 13c Nmr


Q Tbn And9gcszwfrxcq49onmjlxqhhzsgr Bqvobez6hrz0sgx5ne C4dvdwu Usqp Cau


Q Tbn And9gcsosqs9z6 Vehierey1w4gjvtummkv5otwsrvvrz8ez6sn22u 8 Usqp Cau



Dimethylbenzene 1330 7 Wiki


Aromatic Rings Ppt Download
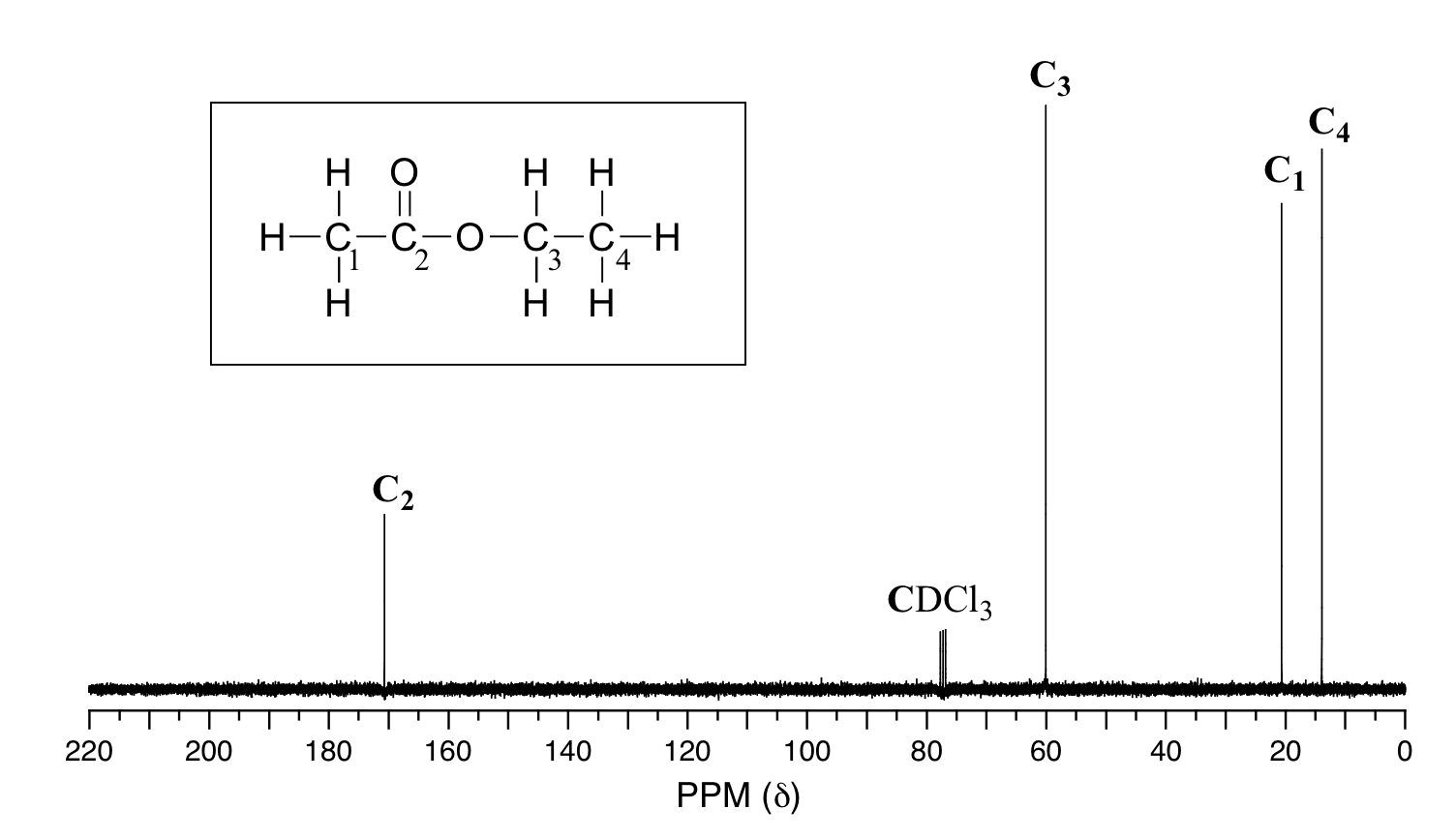


13 11 Characteristics Of C Nmr Spectroscopy Chemistry Libretexts
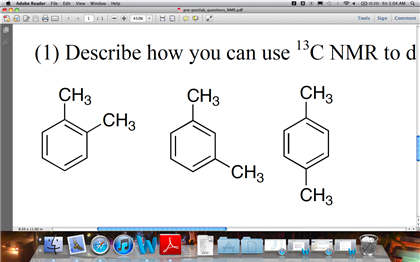


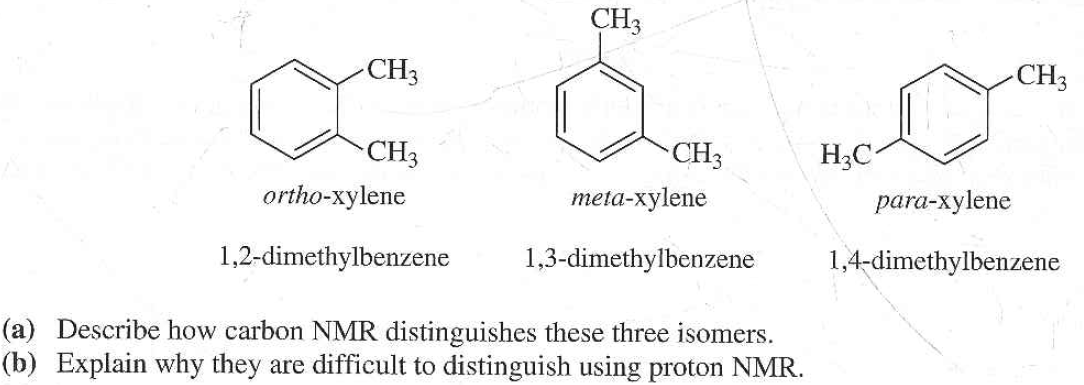
Solved Describe How You Can Use 13c Nmr To Distinguish O Chegg Com


1n 4 Methoxybenzaldehyde Anthony Crasto Spectroscopy
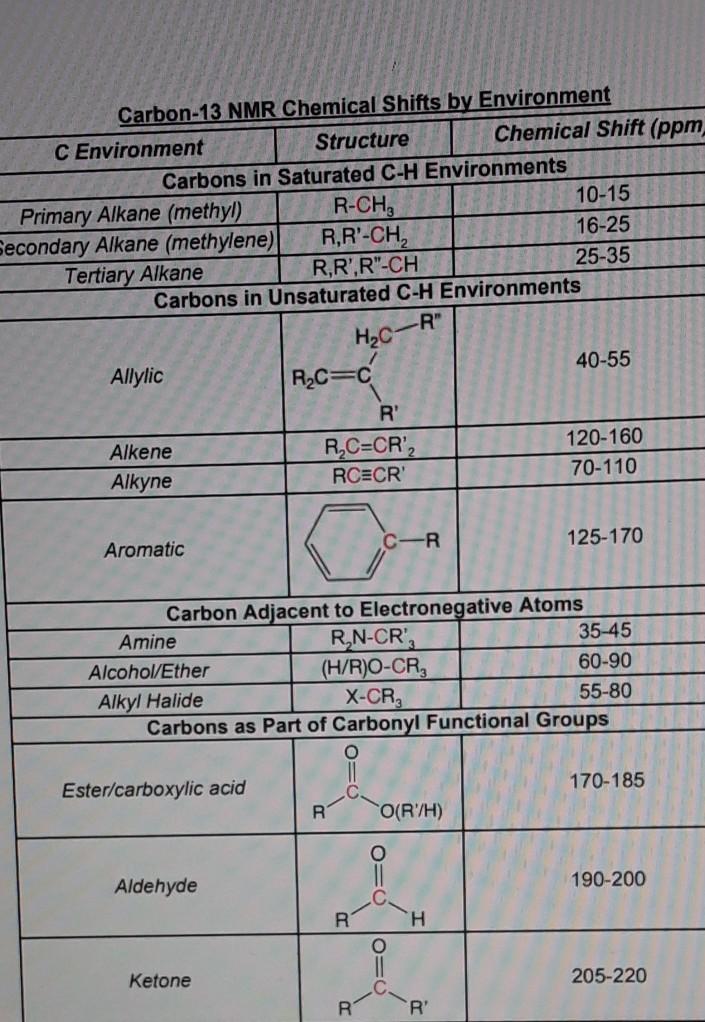


Solved Carbon 13 Nmr 1 Based On The Materials Used There Chegg Com
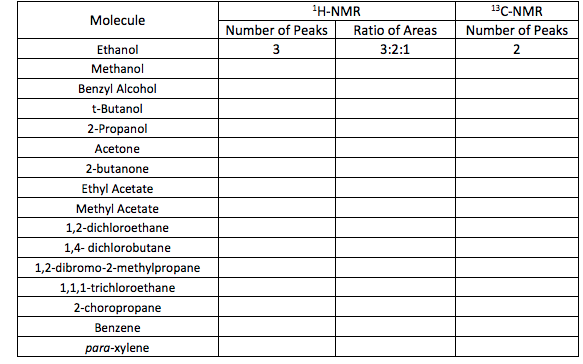


Solved Predict The 1h Nmr And 13c Nmr Spectrum For The Fo Chegg Com
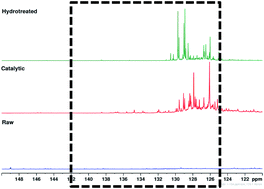


Quantitative 13c Nmr Characterization Of Fast Pyrolysis Oils Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing


P Xylene 13c Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase


2 Chloro P Xylene C8h9cl Pubchem


10 9 Carbon 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Chemistry Libretexts



1h And 13c Nmr Of Some A Halo Derivatives Of O Xylene Sciencedirect
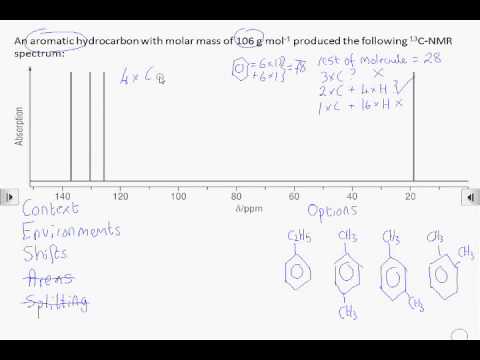


How2 Interpret A Carbon 13 Nmr Spectrum Youtube


Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nmr Spectroscopy An Overview Thespectroscopy



Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Wikipedia
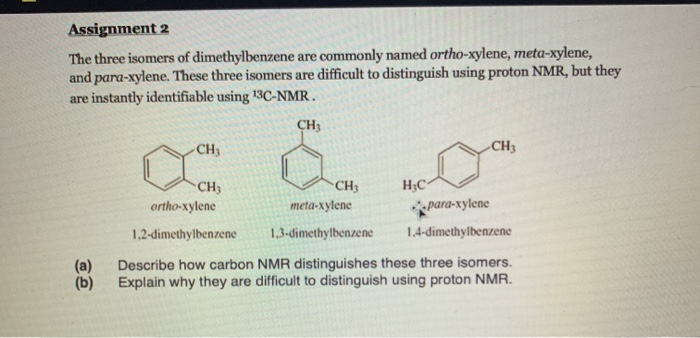


Solved Assignment 2 The Three Isomers Of Dimethylbenzene Chegg Com


Learning Objectives 13 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Ppt Download


Use Of Nmr In Structure Ellucidation
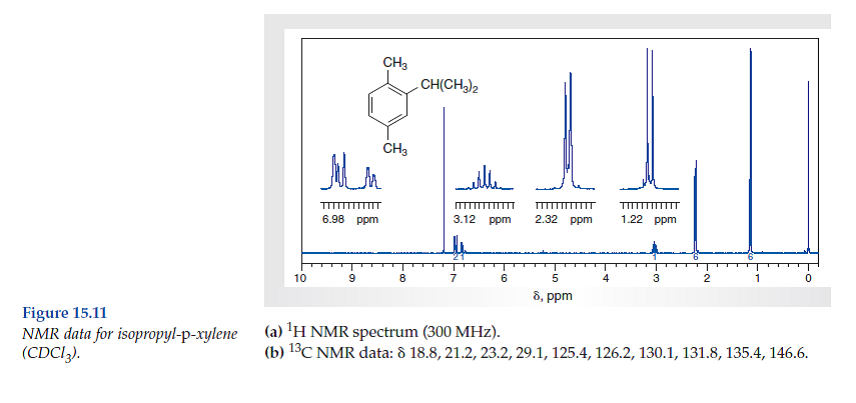


Solved Consider The Spectral Data For Isopropyl P Xylene Figs Chegg Com


Nmr Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
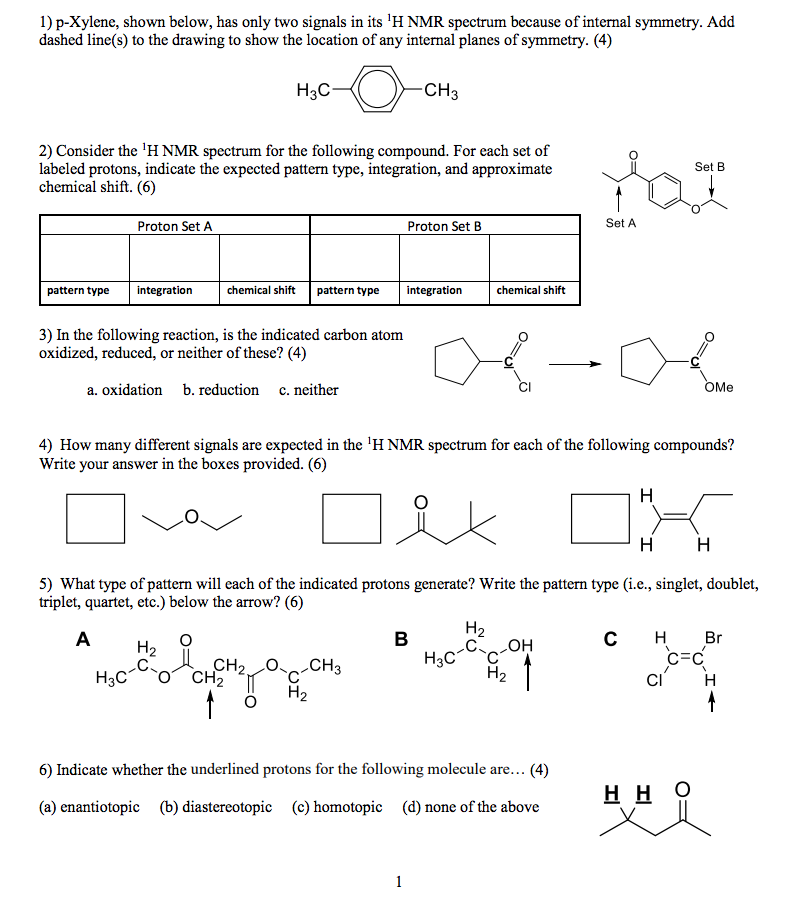


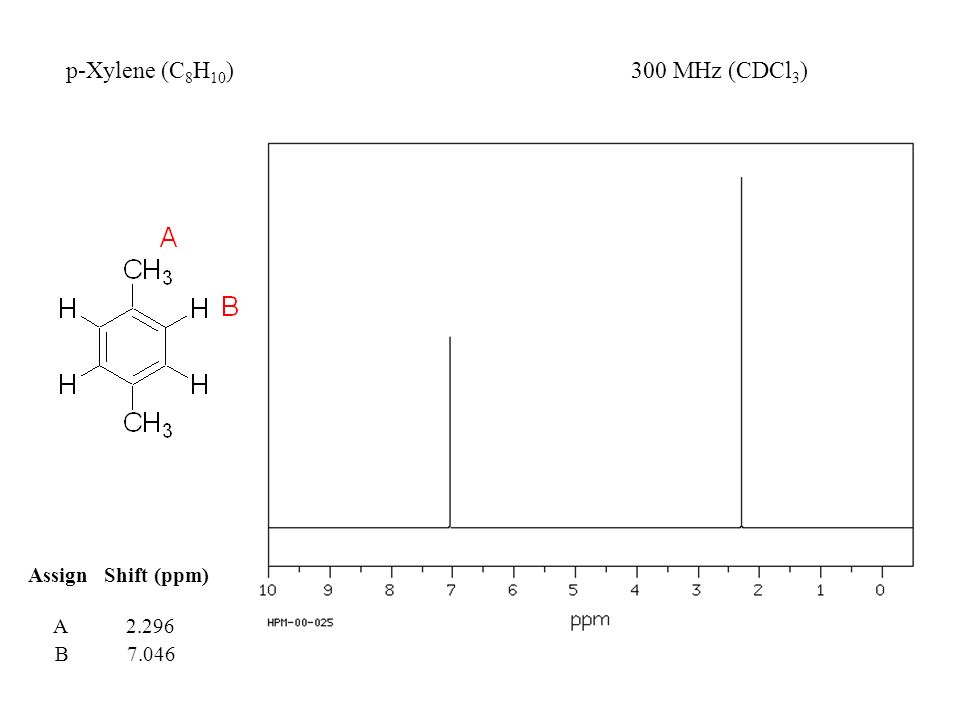
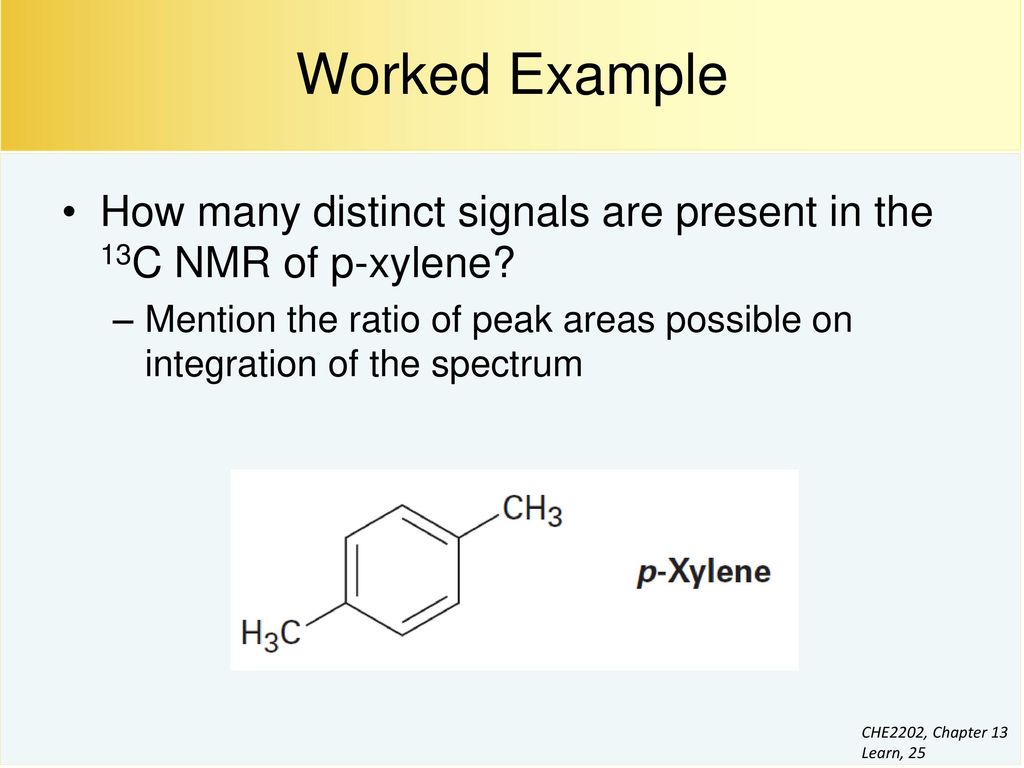
Solved P Xylene Shown Below Has Only Two Signals In Its Chegg Com
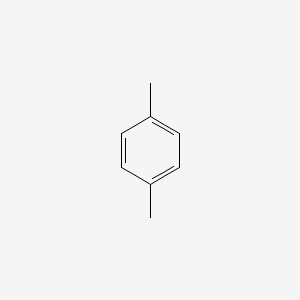


P Xylene C6h4 Ch3 2 Pubchem
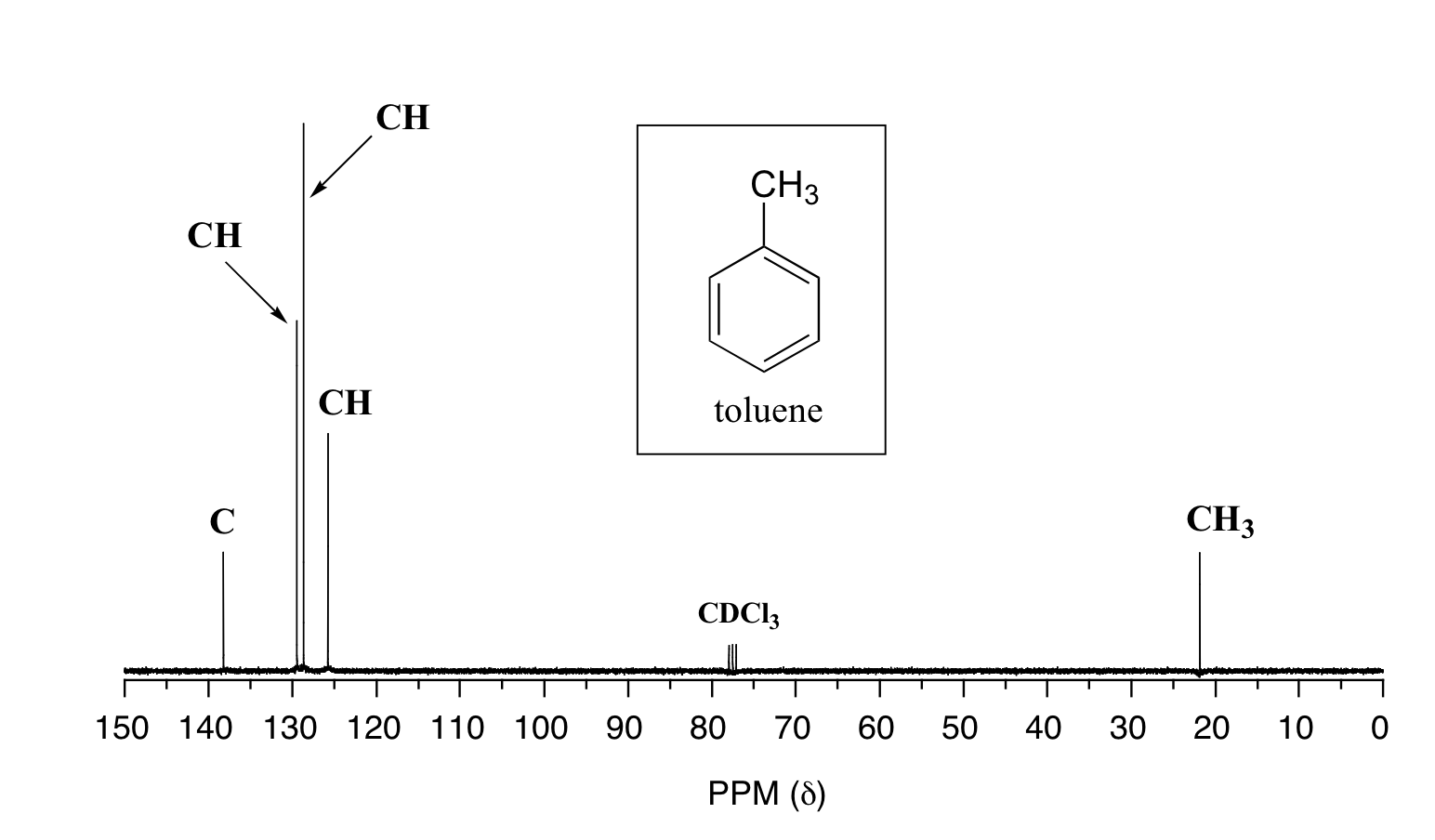


5 6 La Espectroscopia 13c Nmr Libretexts Espanol


Canvas Wisc Edu Courses Files Download Wrap 1



Organic Spectroscopy International 13c Nmr Benzene Toluene


Quiz 13


Http Www Users Miamioh Edu Gungbw Chm255 Html Pdfs Nmr Pdf
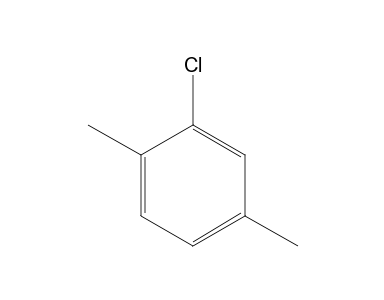


2 Chloro P Xylene 13c Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase



Figure 24 From The Comparison Of Friedel Crafts Alkylation And Acylation As A Means To Synthesise Alkyl Xylenes Semantic Scholar


Http Www Users Miamioh Edu Gungbw Chm255 Html Pdfs Nmr Pdf
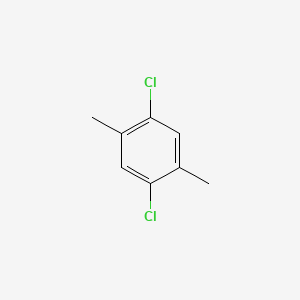


2 5 Dichloro P Xylene C8h8cl2 Pubchem



Proton Nmr Skills Benzene Derivatives Part 1 Youtube



11 Points The 1h Nmr 13c Nmr Mass Spectra And Ir Spectra For A Mystery Homeworklib


C13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance


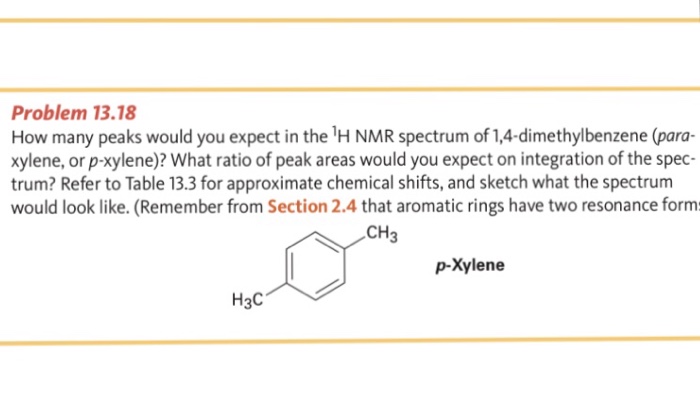
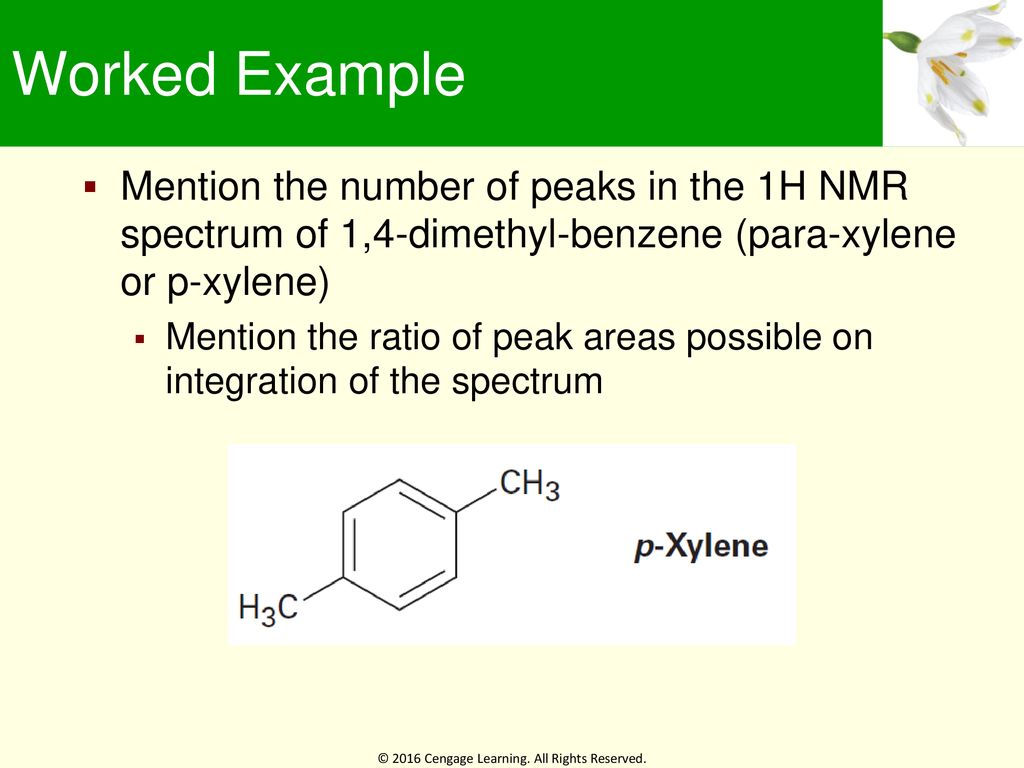
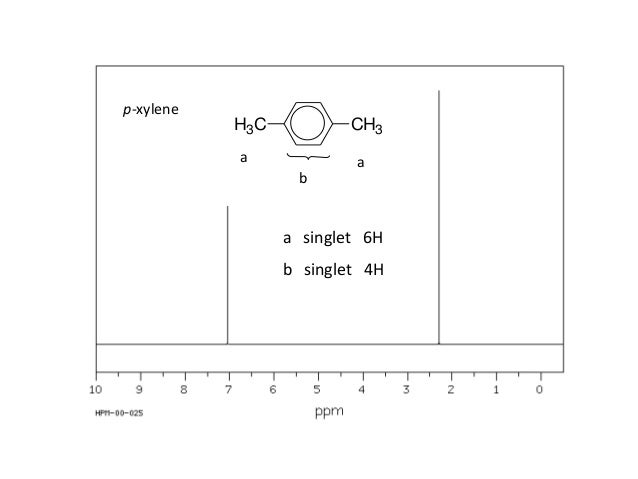
How Many Peaks Would You Expect In The 1 H Nmr Spectrum Of 1 4 Dimethyl Benzene Para Xylene Or P Xylene What Ratio Of Peak Areas Would You Expect On Integration Of
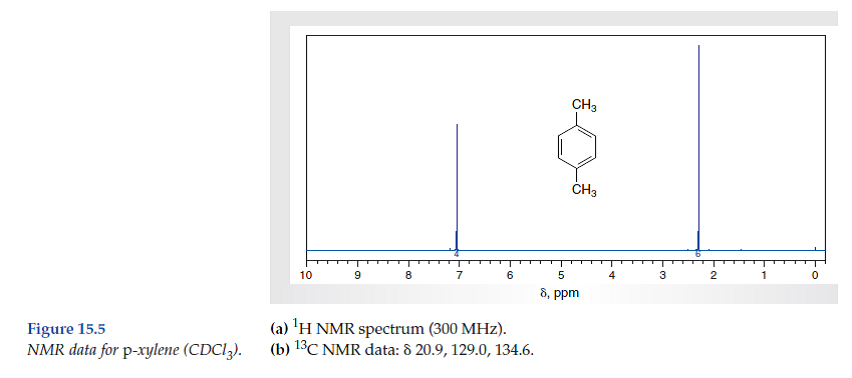


Solved Consider The Spectral Data For P Xylene Figs 15 4 And Chegg Com
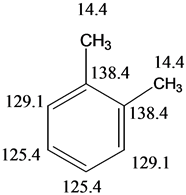


Solved The Three Isomers Of Dimethylbenzene Are Commonly Named Chegg Com
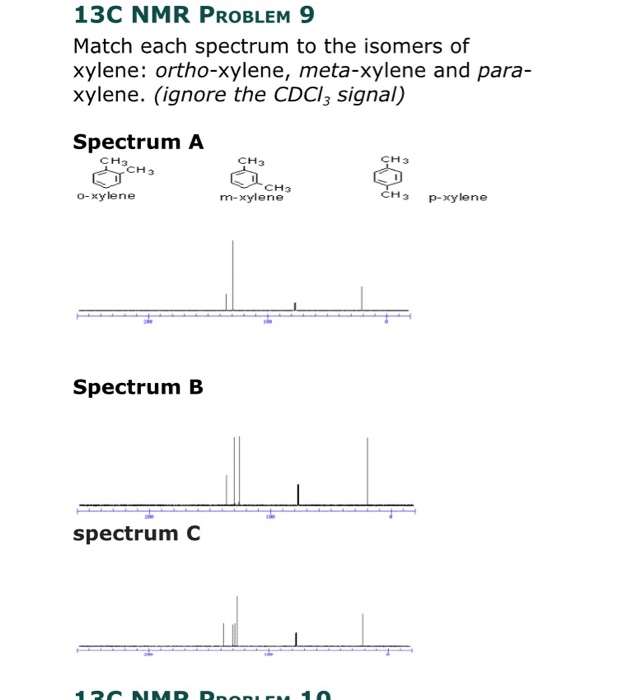


Solved 13c Nmr Problem 9 Match Each Spectrum To The Isome Chegg Com
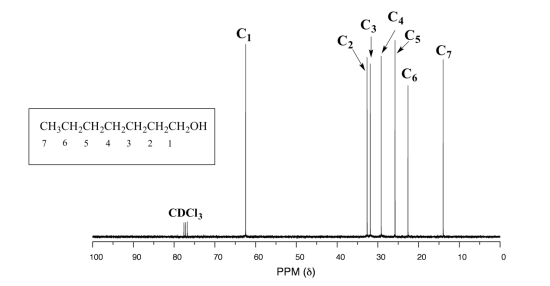


5 6 13c Nmr Spectroscopy Chemistry Libretexts
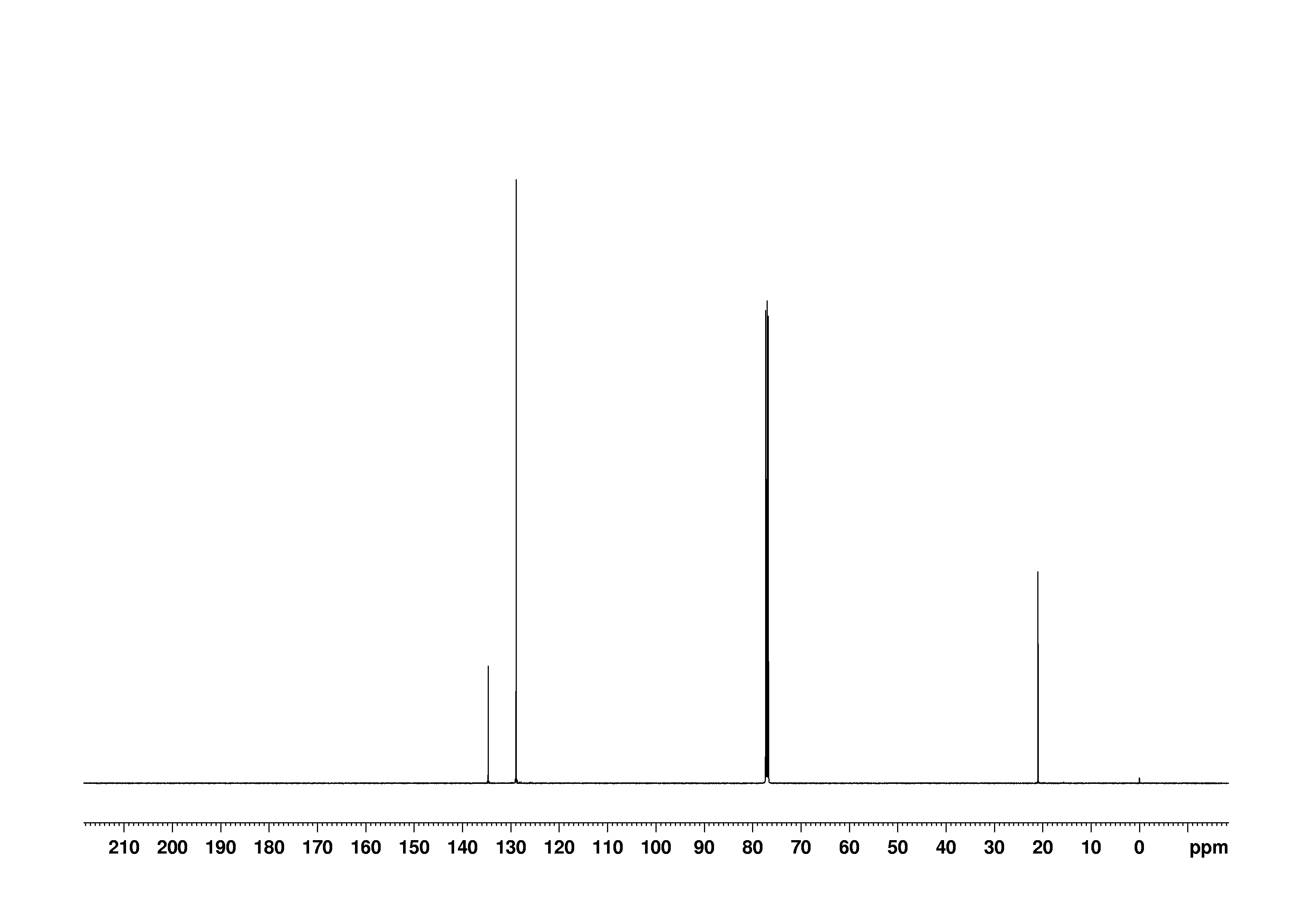


Bmse0004 P Xylene At Bmrb
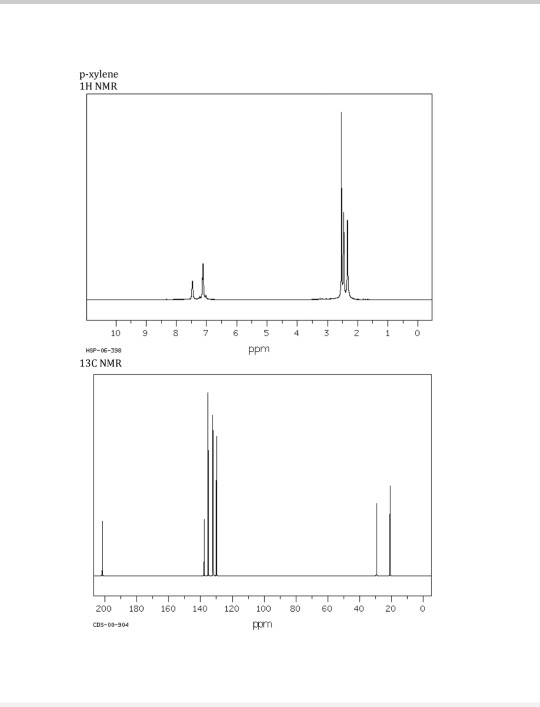


Solved P Xylene 1h Nmr 10 Hsp 06 398 13c Nmr 9 Ppm 0 18 Chegg Com


C13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance



5 6 La Espectroscopia 13c Nmr Libretexts Espanol



Nanopdf Com Chapter 13 Spectroscopy Answers



The High Resolution Solid State 13 C Nmr Spectra Of Sps M Xylene And Download Scientific Diagram


Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nmr Spectroscopy An Overview Thespectroscopy


Q Tbn And9gcqcu80twqv7mdlbqwve41o9dhqvy8ncv9h6olz 4nwlnkztot Usqp Cau


Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nmr Spectroscopy An Overview Thespectroscopy
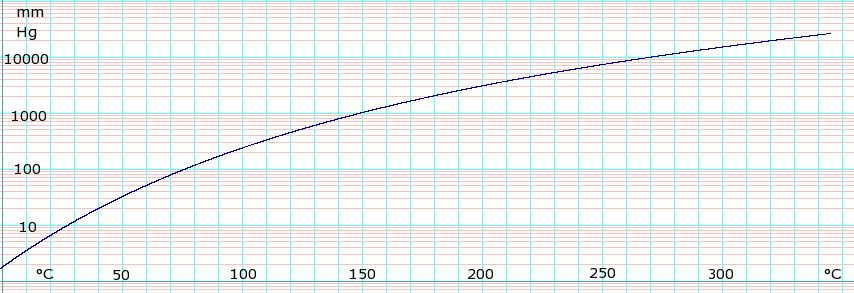


P Xylene Data Page Wikipedia


Www Chem Wisc Edu Deptfiles Orglab Handouts Chem 344 1h Nmr lecture 1 spring 14 Notetaking Pdf


コメント
コメントを投稿